During Glycolysis Glucose Is Broken Down Into What 3-carbon Compound
Carbon dioxide The conversion of a 3-carbon compound into a 2-carbon compound occurs by the removal of ___17___. When the muscles perform vigorous activity and there is less supply of oxygen the cells perform anaerobic type of respiration.

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy
Pyruvate The three-carbon molecule that is the final product of glycolysis is pyruvate.
. Fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids cannot be. Energy is released during glycolysis. In this stage of respiration glucose is converted to pyruvic acid.
Each molecule of glucose produces four molecules of ATP during glycolysis. Pyruvate is a. Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle.
In prokaryotes these processes take. This releases energy which is transferred to ATP. ATP and NADH are produced as part of the process.
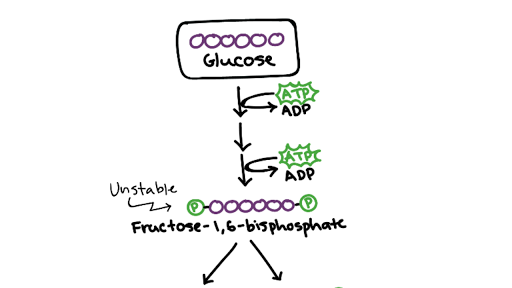
Enzymes split a molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate also known as pyruvic acid. This produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH. During glycolysis the 6-carbon glucose is broken down into two moles of 3-carbon pyruvate via 10 enzyme-catalyzed sequential reactions as shown in the above figure.
This type of fermentation produces carbon dioxide which causes bread dough to rise. The _are the network region of the circulatory system where exchange takes place within the bodys tissue. Acetyl-CoA is a metabolite derived from glucose fatty acid and amino acid catabolism.
The word glycolysis means glucose splitting which is exactly what happens in this stage. A total of 2 NADH are produced. Most of the water we drink is absorbed through the 4.
In glycolysis glucose is converted into pyruvate in the cytoplasm The main organic compound used in cell respiration is carbohydrates glucose although lipids and proteins can be used Lipids are not preferentially used as they are harder to transport and digest although will yield more energy per gram Proteins are not preferentially used as they release potentially. Glycolysis which occurs in the cytosol begins the degradation process by breaking glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate. Can Acetyl-CoA converted to pyruvate.
It occurs almost in all the cells. In glycolysis glucose C6 is split into two 3-carbon C3 pyruvate molecules. Sun -- Photosynthesis -- glucose -- glycolysis anaerobic process -- pyruvate 3-carbon molecule.
There is net production of two molecules of ATP during glycolysis. The oxidation of glucose begins during glycolysis. At the end of the glycolysis reactions what has occurred.
Glucose is phosphorylated at C 6 to yield Glucose 6-phosphate by Hexokinase or. Glucose 6 carbon atoms is split into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid 3 carbons each. After glycolysis pyruvate is broken down into.
What carbon compound is the final product of glycolysis. When oxygen is present and the cell proceeds to aerobic respiration the pyruvic acid is converted into Acetyl Coenzyme A by oxidative decarboxylation. Does glycolysis contain carbon.
Recall that NAD is a coenzyme organic compound required by an. Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytoplasm. During glycolysis glucose is broken down into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate.
This stage of cellular respiration produces hydrogen atoms ATP and carbon dioxide. NAD accepts the electrons during the oxidation and as a result it gets reduced. Glucose a six-carbon compound is broken into two moles of three-carbon keto acid or pyruvic acid.
ATP are generated when hydrogen protons cause a rotor to spin as they flow across the crista membrane through this enzyme. This respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. In eukaryotes pyruvate enters the mitochondrion and is oxidized to a compound called acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose is broken in half producing two molecules of pyruvic acid a 3-carbon compound. Adenosine Triphosphate ATP This molecule serves as a source of immediate energy for cellular process that require energy. 10-2 The Process of Cellular Respiration Glycolysis 1 st step sugar breaking During glycolysis 1 molecule of glucose a 6-carbon compound is transformed into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid a 3-carbon compound.
But two ATP molecules are used to rearrange the glucose molecule. At the end of the electron transport chain low-energy hydrogen electrons and hydrogen protons are. Six-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules pyruvate during glycolysis.
Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. There the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide is completed. Glucose is converted to 3 carbon compound pyruvate by glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular. Glycolysis During glycolysis glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. During glycolysis glucose is broken down into a 3-carbon compound known as 3.
In the absence of oxygen in muscles pyruvate is converted to lactic acid. Breakdown of Glucose Glycolysis Glucose is broken down to pyruvic acid during glycolysis making some ATP. Here are the basics of how cellular respiration works.
During glycolysis glucose is broken down into this 3 carbon compound hydrogen protons during the electron transport chain this is pumped from the matrix across the cristae membrane into the inner membrane space. During the second stage often called the bridge reaction of respiration pyruvic acid is converted into a 2-carbon compound called ___16___. What compounds does glycolysis use.
During glycolysis which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell cells break glucose down into pyruvate a three-carbon compound. The rising phase of an action potential is due to an of Nat along the axon.
2 27 Glycolysis Biology Libretexts

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

9 2 The Process Of Cellular Respiration Flashcards Practice Test Quizlet
Comments
Post a Comment